SI joint stabilization exercises are essential for managing pain and improving joint stability. These exercises target the sacroiliac joint, enhancing mobility and strengthening surrounding muscles to promote long-term relief and functional movement. Regular practice can significantly reduce discomfort and prevent further dysfunction, making them a cornerstone of rehabilitation and proactive care.
1.1 Overview of SI Joint Stabilization
SI joint stabilization involves targeted exercises and techniques to restore balance and strength to the sacroiliac joint. Key components include strengthening the surrounding muscles, improving joint mobility, and enhancing overall pelvic stability. Techniques like pelvic tilts, bridging, and clamshell exercises are commonly used to promote proper alignment and reduce dysfunction. Additionally, tools such as sacroiliac braces and physical therapy modalities can support the process, helping to alleviate pain and improve functional movement. Regular practice of these methods can significantly enhance joint stability and long-term comfort.
1.2 Importance of Stabilization Exercises
Stabilization exercises are crucial for addressing SI joint dysfunction, as they help restore balance, reduce pain, and prevent further instability. These exercises strengthen the muscles around the joint, improving mobility and supporting daily activities. By enhancing pelvic stability, they reduce the risk of repetitive strain and dysfunction. Incorporating techniques like bridging and clamshell exercises, along with tools such as sacroiliac braces, can provide significant relief and empower individuals to manage their condition effectively. Consistency in practice is key to achieving long-term benefits and maintaining joint health.
Understanding the SI Joint
The SI joint connects the sacrum to the ilium bones, playing a vital role in absorbing shock and facilitating movement between the spine and legs. It is supported by ligaments and muscles, providing stability and enabling functional activities like walking and bending. Understanding its structure and function is key to addressing dysfunction and implementing effective stabilization exercises.
2.1 Definition and Function of the SI Joint
The sacroiliac (SI) joint is a complex joint connecting the sacrum and ilium bones, essential for absorbing shock and facilitating movement between the spine and pelvis. It plays a crucial role in weight distribution, enabling activities like walking and bending. The SI joint’s function includes providing stability while allowing limited motion, making it integral to pelvic and lower back mechanics. Its proper function is vital for maintaining posture and preventing dysfunction, which can lead to pain and mobility issues if compromised.
2.2 Location and Structure of the SI Joint
The sacroiliac (SI) joint is located at the base of the spine, connecting the sacrum to the ilium bones of the pelvis. It is a synovial joint enclosed by strong ligaments that provide stability. The joint allows for limited movements, such as flexion, extension, and rotation, essential for activities like walking. Its structure includes a cartilage-lined joint space and surrounding muscles, which work together to support the pelvis and facilitate movement while maintaining balance and stability in the lower back and pelvic region.
2.3 Role of the SI Joint in Movement and Stability
The SI joint plays a crucial role in movement and stability by acting as a bridge between the spine and pelvis. It absorbs shock during activities like walking and running, distributing forces evenly. The joint’s limited mobility allows for controlled pelvic tilting and rotation, essential for maintaining posture and facilitating smooth gait mechanics. Its stability is maintained by strong ligaments and surrounding muscles, ensuring proper biomechanical function and reducing the risk of injury or dysfunction in the lower back and pelvic region.

Causes and Symptoms of SI Joint Dysfunction
SI joint dysfunction often results from trauma, overuse, or structural imbalances. Symptoms include lower back pain, buttock discomfort, and leg radiating pain, along with stiffness or instability.
3.1 Common Causes of SI Joint Instability
SI joint instability often arises from trauma, repetitive strain, or ligament laxity. Activities like heavy lifting, sudden twists, or repetitive movements can disrupt the joint’s alignment. Pregnancy-related hormonal changes can weaken ligaments, increasing instability. Poor posture or muscle imbalances may also contribute, as uneven weight distribution stresses the joint. Additionally, conditions like arthritis or prior injuries can exacerbate instability, leading to pain and dysfunction.
3.2 Symptoms of SI Joint Dysfunction
SI joint dysfunction often presents with lower back or buttock pain, which may radiate to the thighs. Activities like sitting, standing, or lifting can exacerbate symptoms. Patients may experience stiffness, limited mobility, or a feeling of instability in the pelvis. Pain can worsen with prolonged sitting or twisting movements. In some cases, discomfort may be referred to the groin or abdomen. These symptoms can vary in intensity and are often accompanied by difficulty in maintaining proper posture or performing daily activities without discomfort.
3.3 Diagnosis and Assessment of SI Joint Issues
Diagnosing SI joint dysfunction involves a combination of physical examinations, patient history, and imaging. Key assessments include the Fortin Finger Test and palpation for joint tenderness. Pain during specific movements, like FABER or Gaenslen’s tests, may indicate dysfunction. Imaging such as X-rays or MRIs can rule out fractures or degeneration. A thorough evaluation by a healthcare provider, including physical therapists or chiropractors, is crucial for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan to address the root cause of the dysfunction effectively.

Benefits of SI Joint Stabilization Exercises
SI joint stabilization exercises offer pain relief, improved mobility, and enhanced joint stability. They strengthen surrounding muscles, reducing inflammation and promoting long-term functional movement and overall pelvic health.
4.1 Improved Joint Stability
SI joint stabilization exercises enhance the integrity and resilience of the sacroiliac joint by strengthening the surrounding muscles and ligaments. These exercises, such as pelvic tilts and bridging, help restore balance and alignment, reducing excessive movement that can lead to instability. Improved stability minimizes wear and tear on the joint, promoting better shock absorption and weight distribution. Over time, consistent practice can lead to enhanced structural support, making daily activities less stressful on the pelvis and lower back, and reducing the risk of future dysfunction.
4.2 Pain Relief and Reduced Inflammation
SI joint stabilization exercises are highly effective in alleviating pain and reducing inflammation by addressing the root causes of discomfort. Gentle stretches and controlled movements improve joint mobility, decreasing irritation and inflammation. Strengthening the surrounding muscles also provides additional support, minimizing strain on the SI joint. Over time, consistent practice can lead to significant pain reduction and a decrease in inflammatory responses, creating a more stable and comfortable environment for the joint to function effectively without aggravation.
4.3 Enhanced Mobility and Flexibility
SI joint stabilization exercises significantly improve mobility and flexibility by targeting the sacroiliac joint and surrounding tissues. Gentle stretches, such as the piriformis and hip flexor stretches, enhance joint range of motion. Strengthening exercises, like bridging and pelvic tilts, promote balanced muscle function, reducing stiffness. Improved mobility allows for smoother, pain-free movements, while increased flexibility supports overall pelvic and lower back health, making daily activities more comfortable and reducing the risk of further dysfunction.
4.4 Strengthening of Surrounding Muscles
Strengthening the muscles around the SI joint is crucial for stability and pain relief. Exercises like bridging, clamshell, and bird dog target the glutes, core, and pelvic muscles, enhancing their endurance and function. Stronger muscles provide better support to the SI joint, reducing excessive movement and strain. Progressive resistance and controlled movements help build muscle strength without overloading the joint, leading to improved stability and reduced discomfort over time.

Essential Strengthening Exercises for SI Joint Stability
Key exercises include pelvic tilts, bridging, clamshell, and bird dog, focusing on core and pelvic muscle engagement to enhance stability and reduce pain effectively.
5.1 Pelvic Tilts
Pelvic tilts are a foundational exercise for SI joint stability, targeting the muscles and ligaments around the sacroiliac joint. Lie on your back with knees bent, feet flat, and engage your core. Gently tilt your pelvis upward, flattening your lower back against the floor, then release. Repeat slowly, focusing on controlled movements. This exercise strengthens the pelvic floor, improves mobility, and reduces pain. Start with 10-15 repetitions, breathing naturally, and gradually increase as comfort and strength improve.
5.2 Bridging Exercises
Bridging exercises are highly effective for SI joint stabilization, targeting the glutes and lower back muscles. Lie on your back with knees bent and feet flat, engaging your core. Slowly lift your hips toward the ceiling, squeezing your glutes at the top, then lower back down. Perform 12-15 repetitions, focusing on controlled movements. This exercise strengthens pelvic muscles, enhances joint stability, and improves posture. Avoid arching your back; instead, maintain a neutral spine throughout the movement for optimal benefits and injury prevention.
5.3 Clamshell Exercise
The clamshell exercise strengthens the hip abductors and stabilizes the SI joint. Lie on your side with knees bent and feet touching. Slowly lift your top knee while keeping feet together, squeezing your glutes. Hold for 5 seconds, then lower. Perform 12-15 repetitions on each side. This exercise enhances pelvic alignment and reduces instability. Focus on controlled movements to avoid hip flexor activation, ensuring the glutes and outer hips engage properly for maximum benefit and joint stability.
5.4 Bird Dog Exercise
The Bird Dog Exercise enhances core stability and strengthens the muscles around the SI joint. Start on hands and knees, engage your core, and extend one arm and the opposite leg, holding for 5 seconds. Slowly return and repeat on the other side. Perform 10-12 repetitions per side. This exercise improves balance, reduces SI joint strain, and promotes proper pelvic alignment. Focus on maintaining a straight line from head to heel to maximize effectiveness.

Stretching Exercises for SI Joint Mobility
Stretching exercises enhance SI joint mobility by improving flexibility and reducing stiffness. Gentle movements target surrounding muscles, alleviating discomfort and promoting proper joint alignment. Regular practice supports long-term stability.
6.1 Piriformis Stretch
The piriformis stretch targets the piriformis muscle, which runs near the SI joint. Tightness in this muscle can irritate the joint, leading to pain and instability. To perform the stretch, sit on the floor with the affected leg crossed over the other thigh. Gently press the knee toward the opposite shoulder until a stretch is felt. Hold for 20-30 seconds and repeat 2-3 times on each side. This stretch helps reduce muscle tension and improves joint mobility, contributing to SI joint stabilization and pain relief. Regular practice is recommended to maintain flexibility and prevent dysfunction.
6.2 Knee to Chest Stretch
The knee-to-chest stretch is a gentle exercise that helps improve sacroiliac joint mobility and reduce stiffness. Lie on your back, bring one knee toward your chest, and gently rock side to side. This motion promotes joint movement and relaxation. Repeat on the other side. Avoid bouncing or forcing the stretch beyond a comfortable range. If pain occurs, stop the exercise immediately. Regular practice can enhance flexibility and reduce SI joint-related discomfort, supporting overall stabilization and pain relief efforts.
6.3 Hip Flexor Stretch
The hip flexor stretch is a beneficial exercise for improving sacroiliac joint mobility and reducing stiffness. Kneel on one knee with the other foot flat on the ground. Gently push your hips forward, stretching the front of your hip. Hold for 20-30 seconds and repeat on the other side. This stretch helps relieve tightness in the hip flexors, which can contribute to SI joint dysfunction. Avoid bouncing and stop if pain occurs. Regular practice enhances flexibility and supports joint stabilization.
6.4 Cat-Cow Stretch
The Cat-Cow Stretch is a gentle exercise that improves sacroiliac joint mobility and spinal flexibility. Start on your hands and knees, inhaling as you arch your back (Cow Pose) and exhaling as you round your spine (Cat Pose). Repeat for 5-10 breaths. This stretch enhances joint movement, relieves stiffness, and promotes relaxation in the lower back and pelvis. It’s an excellent way to warm up or cool down, supporting SI joint stability without excessive strain. Regular practice can improve posture and reduce discomfort.
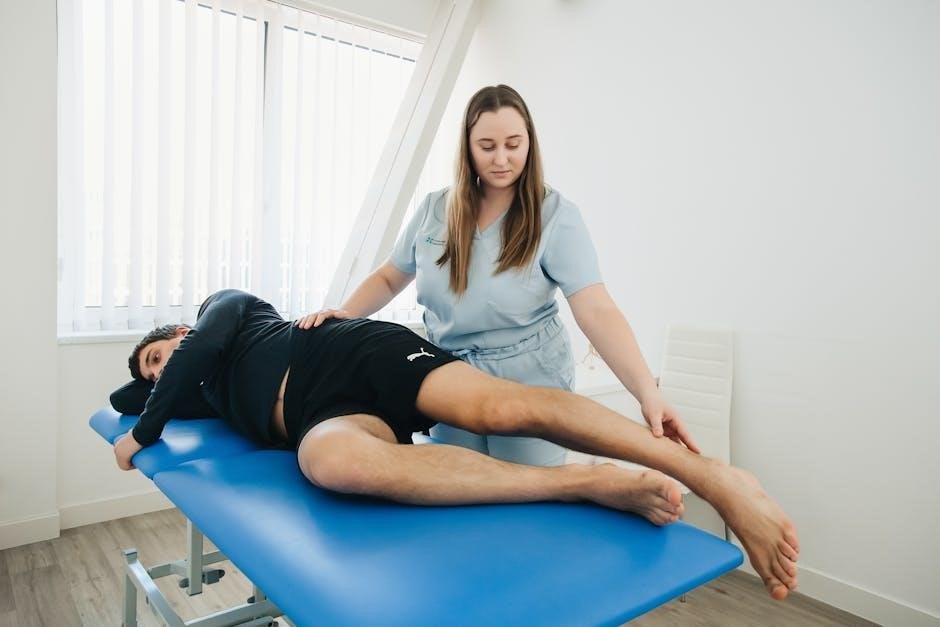
Stabilization Techniques and Tools
Stabilization techniques and tools, such as sacroiliac braces, core strengthening exercises, and physical therapy modalities, are essential for enhancing SI joint stability and reducing discomfort. These methods provide external and internal support, promoting proper alignment and reducing strain on the joint. They are often used alongside exercises for comprehensive care and long-term relief.
7.1 Use of Sacroiliac Braces
Sacroiliac braces are specialized belts or supports designed to stabilize the SI joint. They work by gently compressing the joint, reducing excessive movement and providing structural support. These braces are particularly useful during acute phases of instability or pain, offering immediate relief. By limiting abnormal motion, they help alleviate discomfort and promote healing. Sacroiliac braces are often recommended for individuals with severe instability or those transitioning into exercise programs. They are a valuable adjunct to rehabilitation, enhancing joint stability and reducing pain.
7.2 Core Strengthening Exercises
Core strengthening exercises are vital for SI joint stabilization. They target the muscles of the abdomen, lower back, and pelvis, which play a crucial role in supporting the sacroiliac joint. Strengthening these muscles improves joint stability, reduces pain, and enhances overall mobility. Planks, bird dogs, and pelvic tilts are commonly recommended. These exercises promote proper alignment and reduce strain on the SI joint, fostering a more stable and resilient pelvic structure. Regular core work is essential for long-term joint health and functional movement.
7.3 Physical Therapy Modalities
Physical therapy modalities are effective in addressing SI joint dysfunction. Techniques such as manual therapy, joint mobilization, and soft tissue work can improve joint mobility and reduce stiffness. Heat or ice therapy may be used to alleviate pain and inflammation. Ultrasound and electrical stimulation can also enhance healing and relaxation of tight muscles. These modalities, combined with targeted exercises, help restore proper movement and stability to the SI joint, promoting pain relief and improved functional ability over time.

Progression of Exercises for SI Joint Stability
Progression involves advancing from gentle movements to more challenging exercises, ensuring each stage builds stability and strength, promoting long-term joint health and functional improvement.
8.1 Beginner-Friendly Exercises
Beginner-friendly exercises focus on gentle movements and foundational strength. Pelvic tilts and bridging are excellent starting points, as they improve joint mobility without overexertion. These exercises are typically performed lying down, using body weight for resistance. They help establish a baseline of stability, reducing pain and inflammation. Gradual progression ensures the joints and muscles adapt safely, laying the groundwork for more advanced techniques. Consistency is key to achieving lasting benefits and preventing future dysfunction.
8.2 Intermediate-Level Exercises
Intermediate exercises build on foundational stability, introducing controlled movements and resistance. Bird dog and clamshell exercises enhance core engagement and joint alignment. Resisted knee squeezes and side-lying leg lifts strengthen surrounding muscles. These exercises improve flexibility and reduce stiffness while maintaining joint integrity. Gradual resistance, such as using bands, is incorporated to challenge stability further. Focus on controlled movements to avoid overexertion, ensuring proper form and muscle activation. Consistency helps maintain progress and prevents future dysfunction.
8.3 Advanced Stabilization Techniques
Advanced stabilization techniques involve dynamic balance exercises, single-leg stands, and resistance band work to challenge SI joint stability. These exercises incorporate high-level core integration and multi-planar movements to enhance functional strength. Progressed resistance levels and monitored loading help improve joint resilience. Controlled perturbations and reactive training are also used to refine stability in unpredictable environments. These advanced methods require precision and strength, making them suitable for individuals with a strong foundation in intermediate exercises.

Safety Considerations and Precautions
Avoid overexertion and use proper body mechanics to prevent strain. Stop exercising if pain increases or persists, ensuring exercises are tailored to individual tolerance and medical guidance.
9.1 Avoiding Overexertion
Avoiding overexertion is crucial to prevent aggravating SI joint instability. Start exercises slowly, gradually increasing intensity to avoid strain. Monitor pain levels; if discomfort arises, stop immediately. Proper warm-up and cool-down routines can reduce the risk of overexertion. Consulting a healthcare professional ensures exercises are tailored to individual limits, promoting safe and effective progress without compromising joint stability or overall well-being.
9.2 Proper Body Mechanics
Maintaining proper body mechanics is vital during SI joint exercises to prevent strain and ensure effectiveness. Keep your spine aligned, engage your core, and avoid twisting or bending at the waist. Use supportive props like pillows or mats for comfort and stability. Pay attention to posture during both exercises and daily activities to reduce stress on the SI joint, fostering a balanced and safe approach to rehabilitation and long-term joint health.
9.3 When to Stop Exercising
If you experience sharp pain, numbness, tingling, or discomfort during exercises, stop immediately. Discontinue any movement that worsens symptoms or causes radiating pain. Avoid activities that trigger dizziness or breathing difficulties. It’s crucial to prioritize joint safety and consult a healthcare professional if symptoms persist or intensify. Proper assessment ensures exercises are modified or paused to prevent further irritation and promote healing. Always err on the side of caution to avoid exacerbating SI joint instability.
SI joint stabilization exercises are a vital approach to managing pain and restoring function. Consistent practice, combined with professional guidance, can lead to lasting relief and improved mobility.
10.1 Summary of Key Points
SI joint stabilization exercises are highly effective for managing sacroiliac joint pain and restoring function. These exercises, when performed consistently and guided by professionals, offer significant benefits such as pain relief, improved mobility, and strengthening of surrounding muscles; Utilizing tools like sacroiliac braces and maintaining proper body mechanics further enhance the effectiveness of these exercises. Consistency and attention to safety are crucial for achieving optimal results and preventing further dysfunction.
10.2 Encouragement for Consistent Practice
Consistency is key to achieving lasting relief from SI joint pain. By committing to a regular routine of stabilization exercises, individuals can experience significant improvements in joint stability, pain reduction, and overall mobility. Even small, daily efforts can lead to meaningful progress over time. Encourage patients to embrace these exercises as a long-term investment in their health, fostering a stronger, more resilient body capable of withstanding daily demands without discomfort.

Resources for Further Learning
Explore recommended reading materials, websites, and videos for comprehensive guides on SI joint stabilization exercises, including downloadable PDF resources and expert-led instructional content for deeper understanding.
11.1 Recommended Reading Materials
For in-depth understanding, consider reading “Sacroiliac Joint Dysfunction: Diagnosis and Treatment” by Richard Don Tigny, and “Clinical Orthopedic Rehabilitation” by B. Rotella. These resources provide detailed insights into exercises, stretches, and stabilization techniques. Additionally, downloadable PDF guides like “Sacroiliac Joint Exercises for Pain Relief” offer practical, step-by-step routines. These materials are ideal for both patients and practitioners seeking comprehensive approaches to managing SI joint health and improving mobility effectively.
11.2 Suggested Websites and Videos
Visit YouTube for instructional videos like “Sacroiliac Joint Exercises” by Physiotherapy Tutor. Websites such as Healthline and Pure Physiotherapy offer comprehensive guides. Additionally, watch “SI Joint Stabilization Exercises” by RehabFix and “Piriformis Stretch for SI Joint Pain” by Fitness Blender on YouTube. These resources provide visual demonstrations and detailed instructions for effective SI joint stabilization and pain relief.